Set up onchain valuation
This guide walks through how to set up fully onchain NAV calculations and share pricing for a pool using the Centrifuge Protocol's onchain accounting system. By the end of this guide, your pool will automatically compute the Net Asset Value based on onchain holdings and update the share price on the Hub.
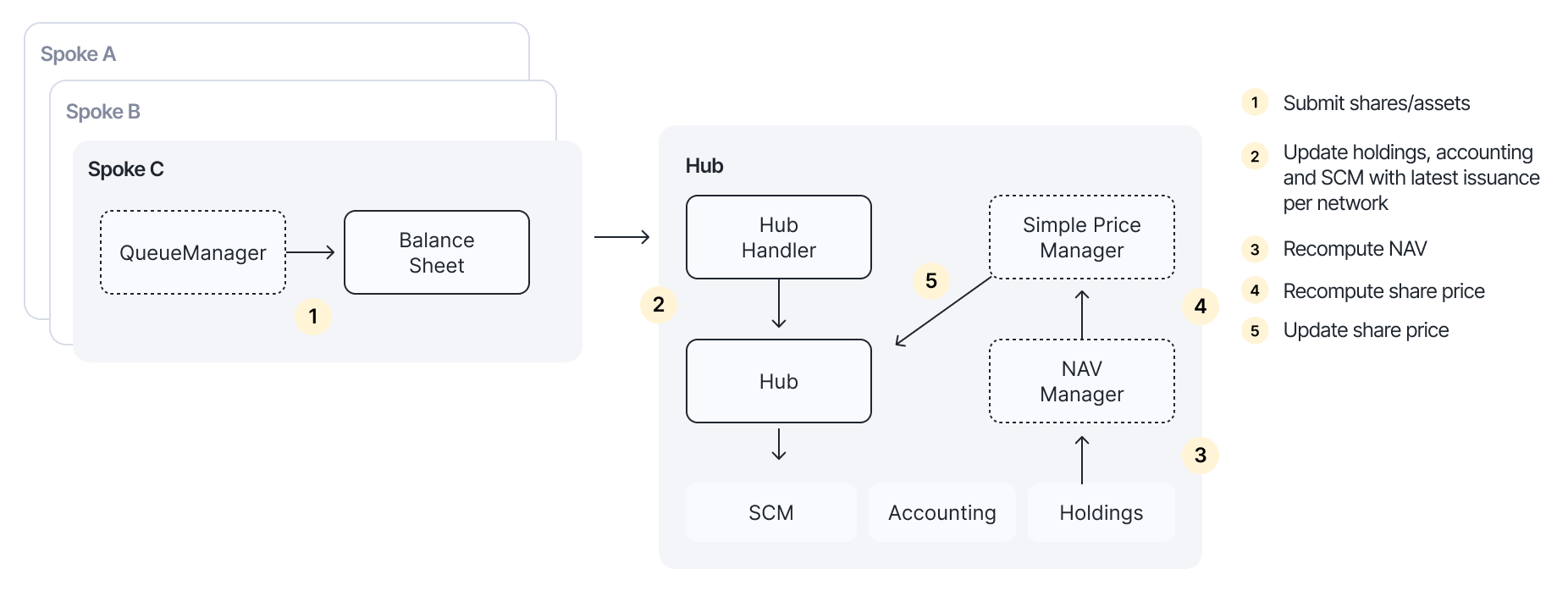
This guide uses a pool with two asset types as an example:
- USDC: An ERC20 stablecoin (priced 1:1 to USD)
- LoanNFT: An ERC6909 token representing a collection of loans, valued by a custom valuation contract
Step 1: Deposit assets into the balance sheet
First, deposit the assets that the pool holds into its balance sheet. This registers them in the protocol's accounting system.
For the ERC20 token (USDC):
usdc.approve(address(balanceSheet), usdcAmount);
balanceSheet.deposit(poolId, scId, address(usdc), 0, usdcAmount);
For the ERC6909 token (LoanNFT):
loanNFT.setOperator(address(balanceSheet), true);
balanceSheet.deposit(poolId, scId, address(loanNFT), tokenId, 1);
The balance sheet supports both ERC20 and ERC6909 tokens. Use token type 0 for ERC20 tokens and a non-zero tokenId for ERC6909 tokens. ERC721 NFTs can be supported by wrapping into ERC6909.
Step 2: Enable Hub Managers
The NAV Manager and Simple Price Manager need to be added as Hub Managers for the pool. This grants them permission to make accounting and price updates.
hub.updateManager(poolId, address(navManager), true);
hub.updateManager(poolId, address(simplePriceManager), true);
Step 3: Enable the Queue Manager
Enable the QueueManager for the pool. The Queue Manager allows permissionless syncing of queued asset and share updates to the Hub, which triggers NAV recomputation through the snapshot hook.
hub.updateBalanceSheetManager(poolId, address(queueManager), true);
Step 4: Initialize the accounting network
Initialize the NAV Manager for the network where the pool's assets are held. This sets up the double-entry bookkeeping accounts needed for NAV computation.
navManager.initializeNetwork(poolId, scId, centrifugeId);
centrifugeId: The network identifier where the assets are deposited
Step 5: Initialize holdings with valuation
Each holding needs a valuation strategy that determines how the asset is priced. Initialize each holding with the appropriate valuation contract.
Fixed-price asset (USDC)
For assets with a stable value pegged 1:1 to the pool currency, use the IdentityValuation contract:
navManager.initializeHolding(poolId, scId, usdcAssetId, address(identityValuation));
The IdentityValuation contract returns the holding quantity as its value, effectively pricing the asset at 1.0 in the pool currency.
Custom-valued asset (LoanNFT)
For assets that require custom pricing logic, such as a portfolio of loans, deploy a contract that implements the IValuation interface:
navManager.initializeHolding(poolId, scId, loanNFTAssetId, address(loanValuation));
Implementing IValuation
Your custom valuation contract must implement the IValuation interface, which has two functions — getPrice and getQuote. For a loan portfolio, the contract should return the total accrued value of all underlying loans:
contract LoanValuation is IValuation {
function getPrice(PoolId poolId, ShareClassId scId, AssetId assetId)
external
view
returns (D18)
{
// Return the price of the asset as a fixed point number with 18 decimals
}
function getQuote(PoolId poolId, ShareClassId scId, AssetId assetId, uint128 baseAmount)
external
view
returns (uint128 quoteAmount)
{
// Calculate and return the value of baseAmount of the asset
// in the pool's denomination currency
}
}
Step 6: Set up the snapshot hook
Connect the NAV Manager as a snapshot hook on the Hub. This ensures that whenever the balance sheet state is updated (e.g. through submitQueuedAssets, submitQueuedShares, or updateHoldingValue), the NAV Manager is automatically triggered to recompute the NAV.
hub.setSnapshotHook(poolId, address(navManager));
Step 7: Set the NAV hook
Set the Simple Price Manager as the NAV hook on the NAV Manager. When the NAV Manager recomputes the NAV (triggered by the snapshot hook), it forwards the result to the Simple Price Manager, which then calculates the share price as NAV / total issuance and calls hub.updateSharePrice.
navManager.setNAVHook(poolId, address(simplePriceManager));
Pushing prices to oracles
After the share price is updated on the Hub, it must be pushed to the price oracle on each network where the pool's share token is deployed. This is done by calling notifySharePrice:
hub.notifySharePrice{value: gas}(poolId, scId, centrifugeId, msg.sender);
gas: The amount of native currency to cover cross-chain messaging costs (excess will be refunded)msg.sender: Address to receive any excess gas refund
This call must be made for each network where the share token is deployed. It can be called after each NAV update or batched at a regular cadence.